Metabolic: From Berlin to Istanbul – building an AI based circularity platform
Circular initiatives platform for 15 major European municipalities
By the end of 2050, European cities and businesses must fully embrace circularity. Many cities have already initiated projects, with some aiming to halve their use of new raw materials by 2030. While all cities and businesses are diligently working toward this complex transformation, they often struggle to chart a winning path tailored to their unique circumstances. Simultaneously, there is a significant opportunity for learning from other cities; however, information is often fragmented and dispersed across various languages.
To address these challenges, Metabolic and Enjins introduce a comprehensive, AI-enabled platform designed to assist cities in assessing their CE baseline, adopt effective strategies, and access localized, up-to-date, actionable information on CE transitions.
Designing and building a Public Service Platform that serves cities and businesses across Europe – from Berlin to Istanbul and from Helsinki to London – presents several challenges. Each city has different data sources, dynamics, and circular initiatives, along with a mix of structured and predominantly unstructured data. This case study focuses on three key questions and shares best practices throughout the process:
- How can we standardize and structure scattered information into a unified language?
- How can we make large data sets accessible in a user-friendly manner while utilizing the latest advancements in generative AI for knowledge retrieval?
- How to realize a transparent and trustworthy AI system in circularity?
”"With this project, we are consolidating all relevant circular economy (CE) knowledge into one dedicated platform."
Jan van ‘t HekProject Manager, Metabolic
The challenge of a shared language: structuring data into a common taxonomy
Cities and businesses struggle to transition to a circular economy due to fragmented and unstructured knowledge. For instance, every city has their own way of expressing their Circular Economy or Sustainable Food strategy. This information is often scattered across different languages and lacks a unified framework or taxonomy, which complicates data access and hinders collaboration among stakeholders.
Without a shared language and taxonomy, leveraging relevant data and engaging in productive discussions to advance circular economy goals becomes difficult. Metabolic addresses this challenge by applying a proven systems-thinking approach that has successfully guided cities and businesses toward circularity. By digitizing a fundamental part of this approach, we together scale the impact of their methodology.
Our AI-powered platform is built around this systems-thinking framework, utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) to organize and interpret extensive data sets. It distils complex information into clear, actionable insights. By incorporating the expertise of Metabolic professionals, the platform ensures that AI-generated outputs are aligned with real-world complexities and validated by circular economy experts, enhancing their accuracy and relevance for urban decision-makers.
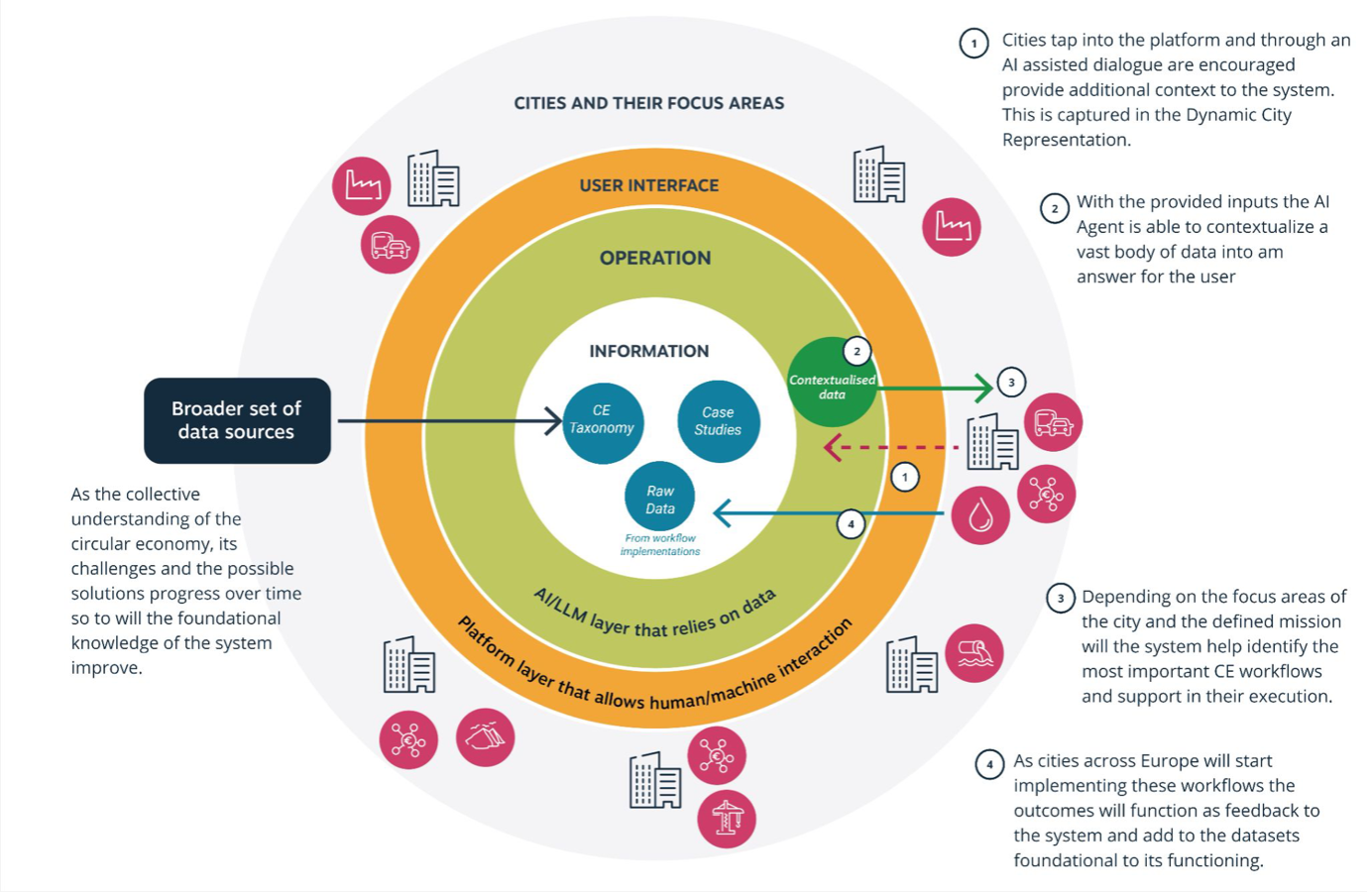
Source: Metabolic
Knowledge retrieval using AI: making information easily accessible
The platform harnesses advanced AI tools to transform user questions into accurate answers. Leveraging the power of AI, it offers three capabilities that extend beyond traditional methods:
- By utilizing advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP), the platform can handle more complex questions and provide nuanced answers. With the latest advancements in generative AI, particularly Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), our AI system surpasses simple keyword matching. It employs Large Language Models (LLMs) to capture semantic meaning, enabling cities and businesses to extract and synthesize relevant information that supports strategic decision-making.
- Unlike a standard ChatGPT approach, the platform incorporates both global and local data, making it specifically tailored for circular economy use cases relevant to each city or business.
- Through continuous improvement driven by new data and user feedback, the AI system adapts to the evolving landscape of circular economy knowledge and the unique needs of various cities. This ensures that the platform remains a dynamic and responsive tool for advancing urban sustainability efforts.
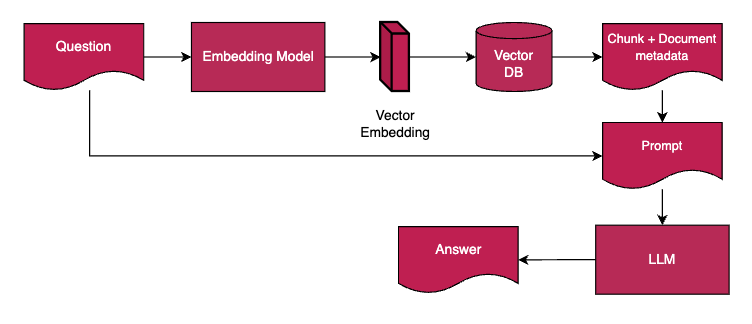
Source: Enjins | from question to answer utilizing AI and tailoring to CE data
Focus on AI Safety and Trustworthy
Given the complexity and responsibility involved in using AI for urban planning and sustainability, ensuring AI safety and trustworthy is a core priority of the platform. Multiple layers have been implemented to ensure reliable and responsible AI use:
- User Interface Design: The platform’s user interface has been carefully designed to support safe and effective interaction. Clear and intuitive workflows guide users in engaging with the system, minimizing the potential for misuse or misunderstanding of data insights.
- Mitigating Hallucinations: One key challenge in AI systems, especially those using large language models, is the risk of generating false or misleading information (often referred to as “hallucinations”). By using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), the platform mitigates this risk by grounding its outputs in verified and relevant data sources, ensuring that the insights presented are reliable and trustworthy.
- Safe and Transparent Instructions through Prompt Engineering: The AI system employs prompt engineering techniques to frame queries and interactions in a way that reduces the chance of erroneous outputs. This ensures that the AI consistently generates responses that are relevant and aligned with the needs of the user.
- Guardrails and Monitoring: Additional guardrails have been built into the system to prevent unintended behaviour. These guardrails limit the AI’s scope to predefined topics and domains, ensuring it remains focused on circular economy insights and preventing it from venturing into unrelated areas. Continuous monitoring of the AI’s performance further ensures that any issues are quickly identified and addressed, maintaining the system’s reliability and safety.
Through this multi-layered approach to AI safety and trustworthiness, the platform provides a secure and trustworthy environment for users to explore and implement circular economy strategies, empowering cities to make informed and responsible decisions on their sustainability journey.
For more information, check out: https://circularpsp.eu/cirrus/
CircularPSP project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Programme under Grant Agreement n° 101092208. (edited)


 Follow us on LinkedIn!
Follow us on LinkedIn! Check out our Meetup group!
Check out our Meetup group!